California Pest Rating for
An Ant | Pheidole dentigula
Hymenoptera: Formicidae
Pest Rating: A
PEST RATING PROFILE
Initiating Event:
Pheidole dentigula was frequently intercepted in 2016 and 2017 by CDFA and requires a pest rating proposal to support an official pest rating.
History & Status:
Background: Pheidole dentigula is a common ant found in leaf litter and rotting stumps in mesic forests of the southeastern United States. They can be recognized in the field by the tendency of the major workers to have orange-colored gasters1.
Pheidole dentigula is associated with moisture-retentive microhabitats and nests in soil and rotten stumps3.
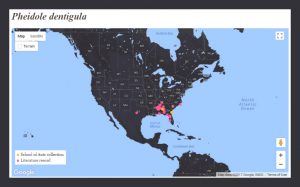
Worldwide Distribution: Pheidole dentigula is known from the United States and Central and South America. In the United States, it is reported from Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Texas3.
Official Control: Pheidole dentigula is not known to be under official control in any states or nations, but the genus Pheidole is listed as a harmful organism in Japan and Republic of Korea5.
California Distribution: Pheidole dentigula has never been found in the environment of California.
California Interceptions: Pheidole dentigula was intercepted 18 times in 2015, 2016, and 2017 by CDFA’s border station and nursery regulatory inspections. Interceptions were typically on plants or plant material imported from the southeastern infested States4.
The risk Pheidole dentigula would pose to California is evaluated below.
Consequences of Introduction:
1) Climate/Host Interaction: Pheidole dentigula is found in moisture-retentive microhabitats, including rotten stumps and accumulations of leaf litter in forests. Riparian areas in California would be suitable for this ant and it could establish in a limited area in California. It receives a Low (1) in this category.
Evaluate if the pest would have suitable hosts and climate to establish in California:
– Low (1) Not likely to establish in California; or likely to establish in very limited areas.
– Medium (2) may be able to establish in a larger but limited part of California.
– High (3) likely to establish a widespread distribution in California.
2) Known Pest Host Range: Pheidole dentigula feeds on dead insects, dead leaves, and decaying fruit. It receives a High (3) in this category.
Evaluate the host range of the pest.
– Low (1) has a very limited host range.
– Medium (2) has a moderate host range.
– High (3) has a wide host range.
3) Pest Dispersal Potential: There is little information available on the biology of Pheidole dentigula. Other members of the genus are known to have multiple queens and are capable of producing large numbers of eggs. Because this may be true for this species, P. dentigula receives at High (3) in this category
Evaluate the natural and artificial dispersal potential of the pest.
– Low (1) does not have high reproductive or dispersal potential.
– Medium (2) has either high reproductive or dispersal potential.
– High (3) has both high reproduction and dispersal potential.
4) Economic Impact: Pheidole dentigula is not expected to lower crop yields or increase crop production costs. It is not expected to disrupt any markets for Californian agricultural commodities. It is not expected to change cultural practices or vector other pestiferous organisms. These ants could injure livestock if established in California. It receives a Low (1) in this category.
Evaluate the economic impact of the pest to California using the criteria below.
Economic Impact: F
A. The pest could lower crop yield.
B. The pest could lower crop value (includes increasing crop production costs).
C. The pest could trigger the loss of markets (includes quarantines).
D. The pest could negatively change normal cultural practices.
E. The pest can vector, or is vectored, by another pestiferous organism.
F. The organism is injurious or poisonous to agriculturally important animals.
G. The organism can interfere with the delivery or supply of water for agricultural uses.
Economic Impact Score: 1
– Low (1) causes 0 or 1 of these impacts.
– Medium (2) causes 2 of these impacts.
– High (3) causes 3 or more of these impacts.
5) Environmental Impact: Pheidole dentigula is not likely to disrupt natural communities, lower biodiversity, or change ecosystem processes in California. This species does not directly impact any threatened species. However, it is likely to trigger new treatments by residents if it invades homes in search of food and water. It receives a Medium (2) in this category
Evaluate the environmental impact of the pest on California using the criteria below.
Environmental Impact: D
A. The pest could have a significant environmental impact such as lowering biodiversity, disrupting natural communities, or changing ecosystem processes.
B. The pest could directly affect threatened or endangered species.
C. The pest could impact threatened or endangered species by disrupting critical habitats.
D. The pest could trigger additional official or private treatment programs.
E. The pest significantly impacts cultural practices, home/urban gardening or ornamental plantings.
Environmental Impact: Score 2
– Low (1) causes none of the above to occur.
– Medium (2) causes one of the above to occur.
– High (3) causes two or more of the above to occur.
Consequences of Introduction to California for Pheidole dentigula: Medium (10)
–Low = 5-8 points
–Medium = 9-12 points
–High = 13-15 points
6) Post Entry Distribution and Survey Information: Pheidole dentigula has never been found in the natural environment in California and receives a Not established (0) in this category.
Evaluate the known distribution in California. Only official records identified by a taxonomic expert and supported by voucher specimens deposited in natural history collections should be considered. Pest incursions that have been eradicated, are under eradication, or have been delimited with no further detections should not be included:
Score: 0
–Not established (0) Pest never detected in California, or known only from incursions.
-Low (-1) Pest has a localized distribution in California, or is established in one suitable climate/host area (region).
-Medium (-2) Pest is widespread in California but not fully established in the endangered area, or pest established in two contiguous suitable climate/host areas.
-High (-3) Pest has fully established in the endangered area, or pest is reported in more than two contiguous or non-contiguous suitable climate/host areas.
Final Score:
The final score is the consequences of introduction score minus the post entry distribution and survey information score: Medium (10)
Uncertainty:
There have not been any formal surveys for Pheidole dentigula in California. This species has been intercepted through regulatory pathways multiple times and can be transported on commodities. It is possible that it might be present in certain areas of California, but if so, it has escaped detection.
Conclusion and Rating Justification:
Pheidole dentigula has never been found in the environment of California. If it were to establish in the state, this ant may have an environmental impact in riparian and wetland areas of California. Other species of this genus have multiple queens and have proved invasive in areas where they are introduced. Given these considerations, an “A”-rating is justified, especially as there is a chance of excluding it.
References:
- Ants (Formicidae) of the Southeastern United states by Joe McGowan. Accessed November 4, 2017. http://mississippientomologicalmuseum.org.msstate.edu/Researchtaxapages/Formicidaepages/genericpages/Pheidole.dentigula.html#.Wfn2_ltSzA4
- Ant web. Accessed November 4, 2017. https://www.antweb.org/description.do?name=dentigula&genus=pheidole&rank=species&project=allantwebants
- School of Ants. Accessed November 4, 2017. http://www.schoolofants.org/species/2155
- Pest and Damage Record Database, California Department of Food and Agriculture, Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services. http://phpps.cdfa.ca.gov/user/frmLogon2.asp
- USDA Phytosanitary Certificate Issuance & Tracking System (PCIT) Phytosanitary Export Database (PExD). Accessed December 23, 2016 https://pcit.aphis.usda.gov/pcit/
Author:
Javaid Iqbal, California Department of Food and Agriculture; 1220 N Street, Sacramento, CA 95814; Tel. (916) 403-6695; plant.health[@]cdfa.ca.gov.
Responsible Party:
Jason Leathers, 2800 Gateway Oaks, Sacramento CA 95833, (916) 654-1211, plant.health[@]cdfa.ca.gov
Comment Period:* CLOSED
4/13/18 – 5/28/18
*NOTE:
You must be registered and logged in to post a comment. If you have registered and have not received the registration confirmation, please contact us at plant.health[@]cdfa.ca.gov.
Comment Format:
♦ Comments should refer to the appropriate California Pest Rating Proposal Form subsection(s) being commented on, as shown below.
Example Comment:
Consequences of Introduction: 1. Climate/Host Interaction: [Your comment that relates to “Climate/Host Interaction” here.]
♦ Posted comments will not be able to be viewed immediately.
♦ Comments may not be posted if they:
Contain inappropriate language which is not germane to the pest rating proposal;
Contains defamatory, false, inaccurate, abusive, obscene, pornographic, sexually oriented, threatening, racially offensive, discriminatory or illegal material;
Violates agency regulations prohibiting sexual harassment or other forms of discrimination;
Violates agency regulations prohibiting workplace violence, including threats.
♦ Comments may be edited prior to posting to ensure they are entirely germane.
♦ Posted comments shall be those which have been approved in content and posted to the website to be viewed, not just submitted.
Pest Rating: A
Posted by ls